Software Preprocessing Settings
Software preprocessing involves processing the data after it has been transferred and before it is made available to the user.
The software preprocessing settings interface is shown in Figure 1:
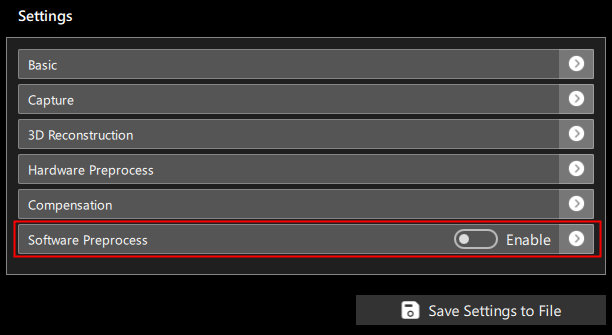
Preprocessing can be enabled or disabled using the Enable control.
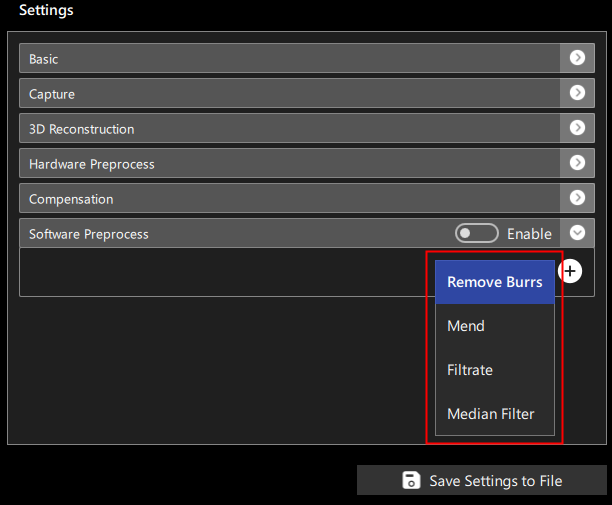
Click the button in the bottom right to add a new set of software preprocessing settings. The currently available types of software preprocessing settings are:
- Remove Burrs
- Mend
- Filtrate
- Median Filter
The interface for selecting the type of preprocessing is shown in Figure 2:
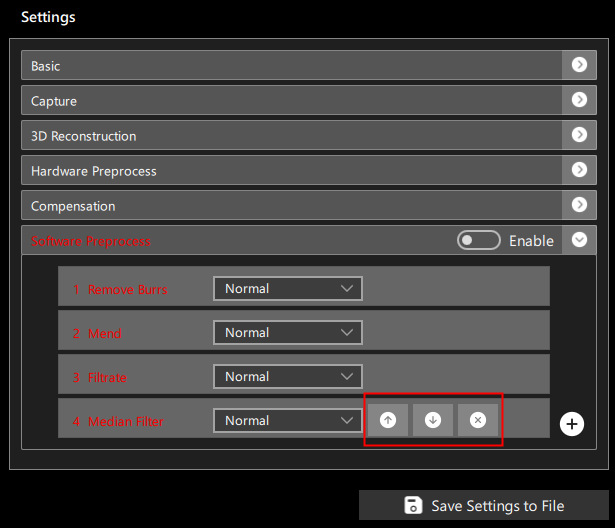
You can manage the order of software preprocessing operations, moving them up or down one line, or deleting them, as shown in Figure 3:
Remove Burrs
Removing burrs is based on the criterion that points not close to their neighbors are likely to be outliers. By adjusting the window size, you can handle different sizes of outlier clusters; adjusting the neighbor threshold, neighbor count, slope, and edge suppression can make the criteria for determining outliers stricter or more lenient. The higher the parameter, the stricter the criteria.
 | 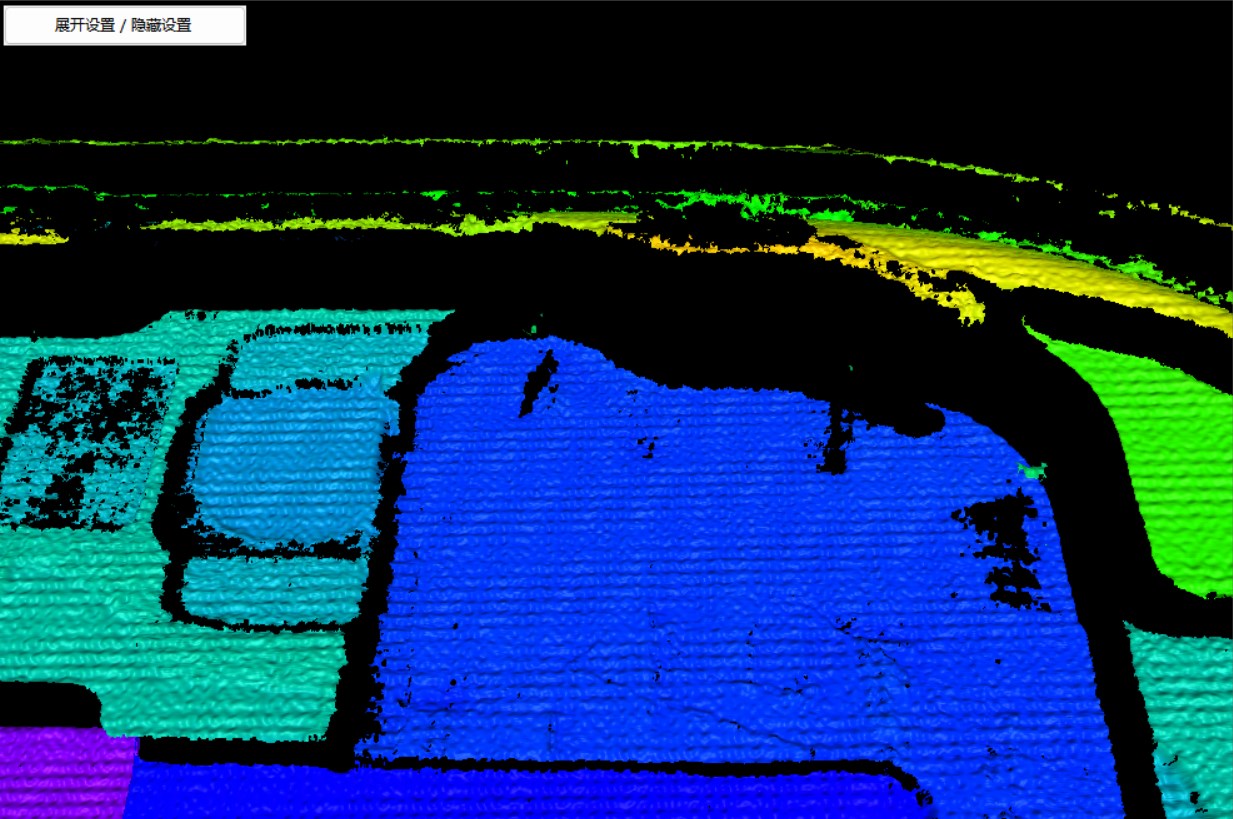 |
|---|---|
| Figure 4: Before Removing Burrs | Figure 5: After Removing Burrs |
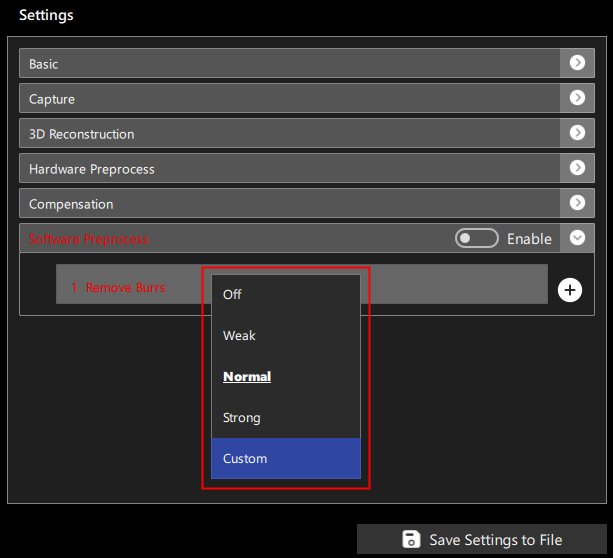
Five modes are available:
- Off: Disables the current preprocessing item
- Weak: Uses a set of preset parameters corresponding to Weak mode on the device
- Normal: Uses a set of preset parameters corresponding to Normal mode on the device
- Strong: Uses a set of preset parameters corresponding to Strong mode on the device
- Custom: Manually set the parameters for removing burrs
As shown in Figure 6:
When Custom mode is selected, you can manually set the parameters for removing burrs, as shown in Figure 7:
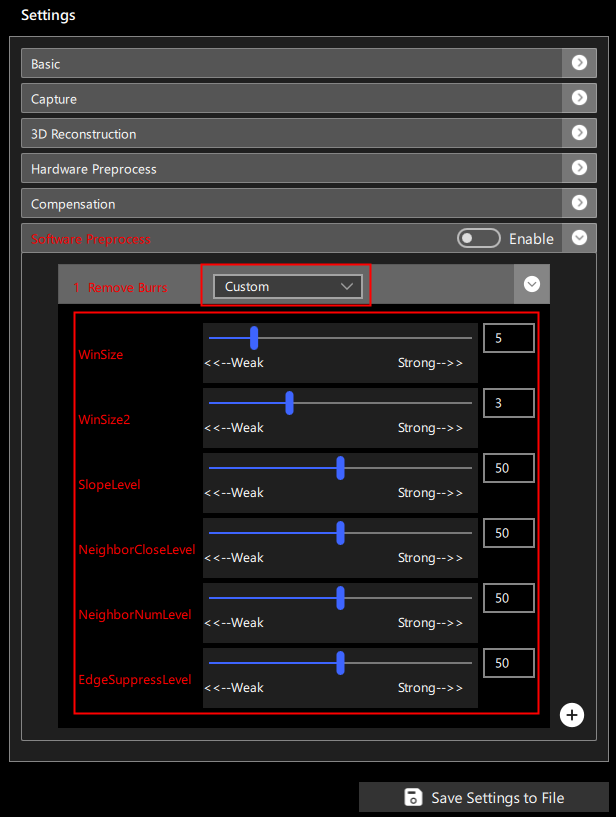
Parameters include:
-
Window Size (WinSize): The range for neighboring points, values from 0 to 31, the larger the value, the more outliers are removed.
(Software default presets: Weak-3, Normal-5, Strong-10)
-
Secondary Window Size (WinSize2): The range for finding related points based on neighboring points, values from 0 to 10, the smaller the value, the more outliers are removed.
(Software default presets: Weak-2, Normal-3, Strong-5)
-
Slope Level: The slope parameter for neighboring points, range from 0 to 100, the larger the value, the more outliers are removed.
(Software default presets: Weak-40, Normal-50, Strong-60)
-
Neighbor Close Level: The parameter for judging the closeness of neighboring points, range from 0 to 100, the larger the value, the more outliers are removed.
(Software default presets: Weak-40, Normal-50, Strong-60)
-
Neighbor Num Level: The number parameter for close neighboring points, range from 0 to 100, the larger the value, the more outliers are removed.
(Software default presets: Weak-40, Normal-50, Strong-60)
-
Edge Suppress Level: The edge suppression parameter, range from 0 to 100, the larger the value, the more outliers are removed.
(Software default presets: Weak-40, Normal-50, Strong-60)
Mend
Mending invalid points uses neighboring points for estimation, either by interpolation or dilation methods. Dilation is suitable for filling vertical edges but can produce burrs; the larger the window, the larger the holes it can mend, but it might also fill genuine holes.
 | 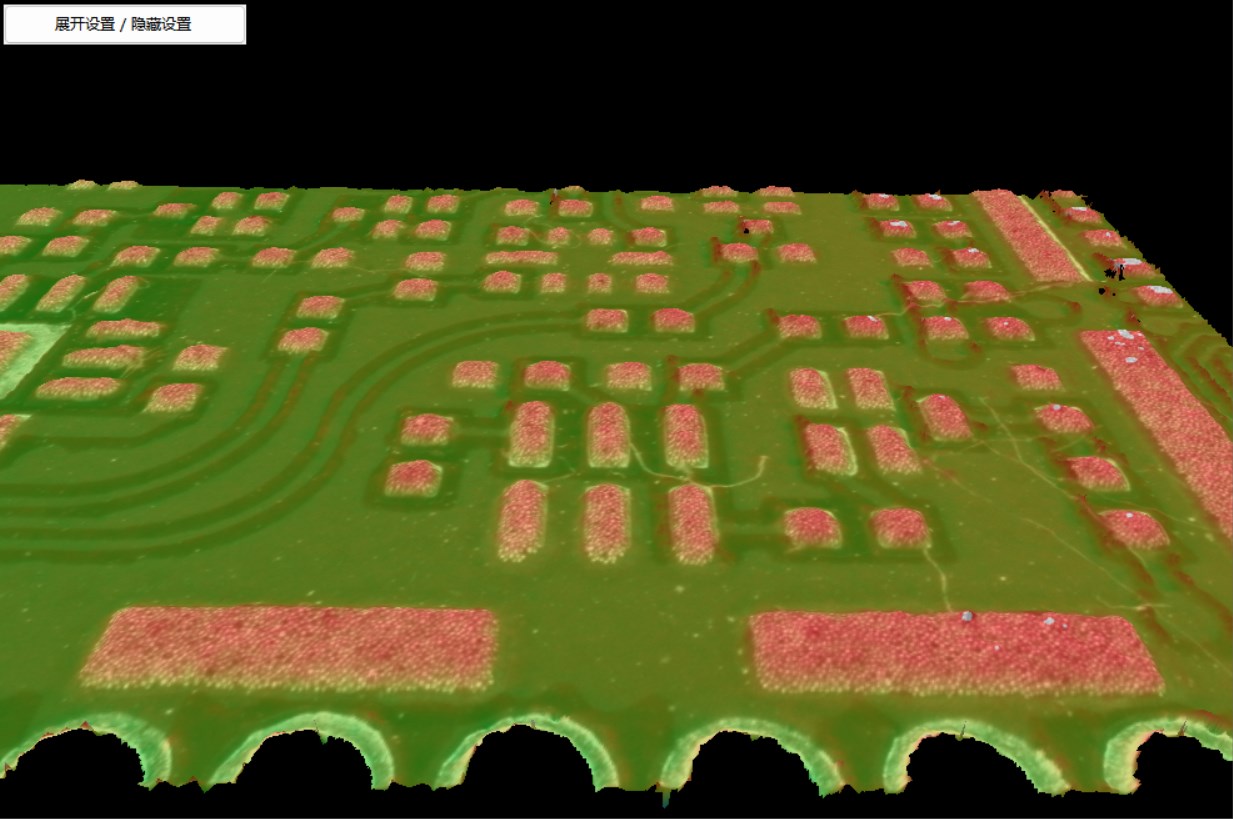 |
|---|---|
| Figure 8: Before Mending | Figure 9: After Mending |
Five modes are available, similar to removing burrs. Off means the current setting is not enabled, while Weak, Normal, Strong use the device's preset parameters. Custom means manually setting the parameters.
When Custom mode is selected, you can manually set the parameters for mending, as shown in Figure 10:
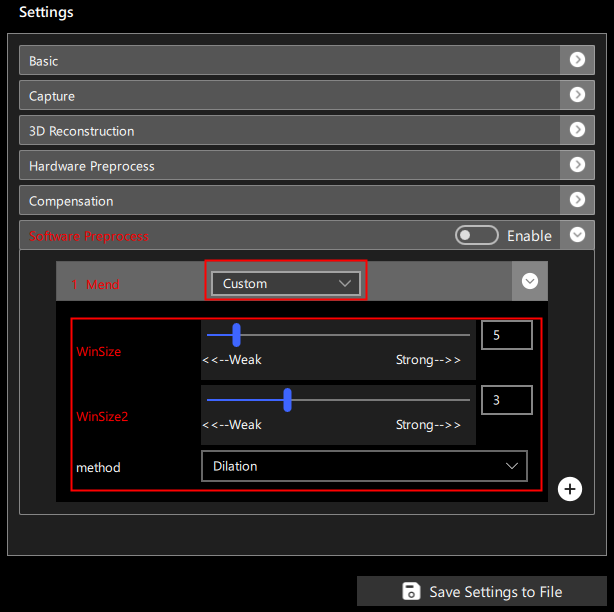
Parameters include:
-
Window Size (WinSize): The range for neighboring points, values from 0 to 50, the larger the value, the more it mends.
(Software default presets: Weak-3, Normal-5, Strong-10)
-
Secondary Window Size (WinSize2): The extra range for neighboring points in the dilation method, values from 0 to 10, the larger the value, the more it mends.
(Software default presets: Weak-2, Normal-3, Strong-5)
-
Method (Method): Two methods are available: 1. Dilation 2. Interpolation; preset values are 0 for Dilation, 1 for Interpolation.
(Software default presets: Weak-1, Normal-1, Strong-1)
Filtrate
The smoothing method uses averaging of neighboring points to process 3D data, the larger the window, the larger the range of points participating in averaging; points that do not meet the neighbor threshold and neighbor count threshold are not smoothed, adjusting these thresholds can preserve true height transitions.
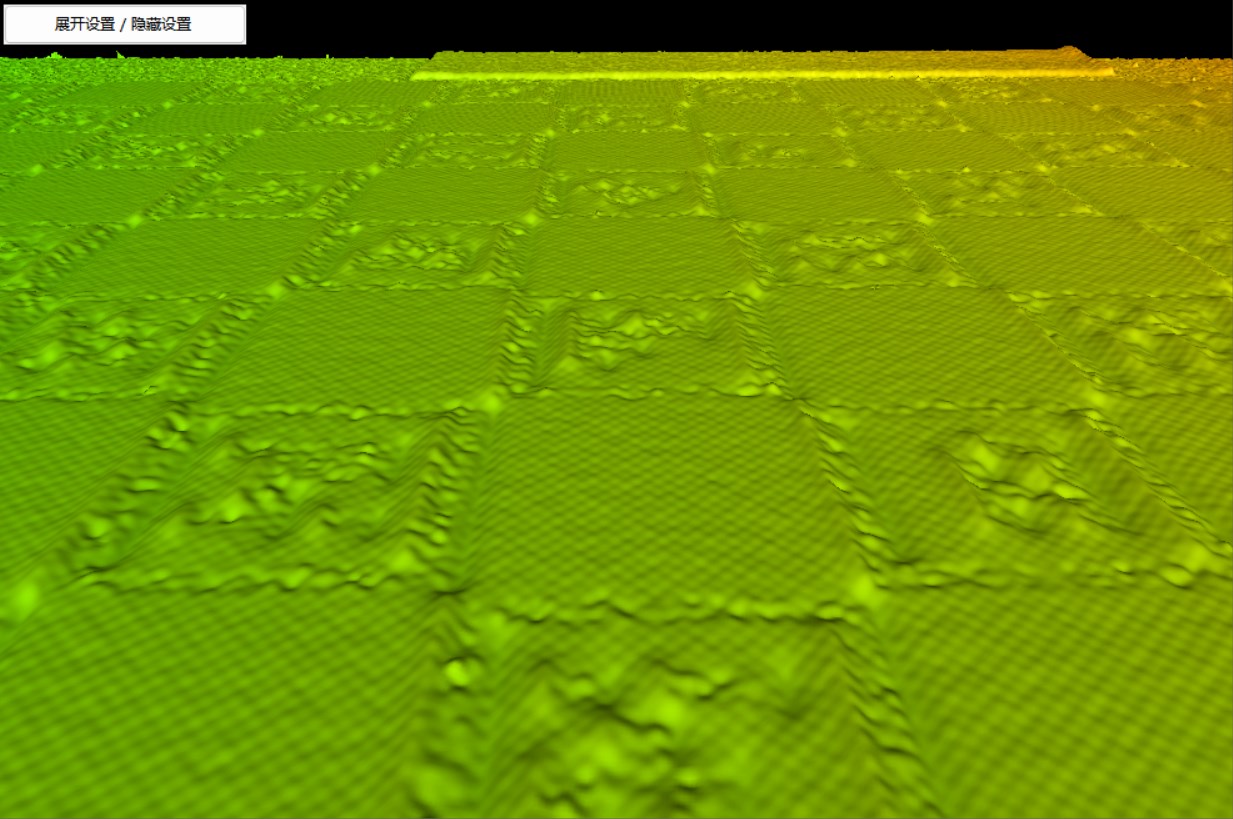 | 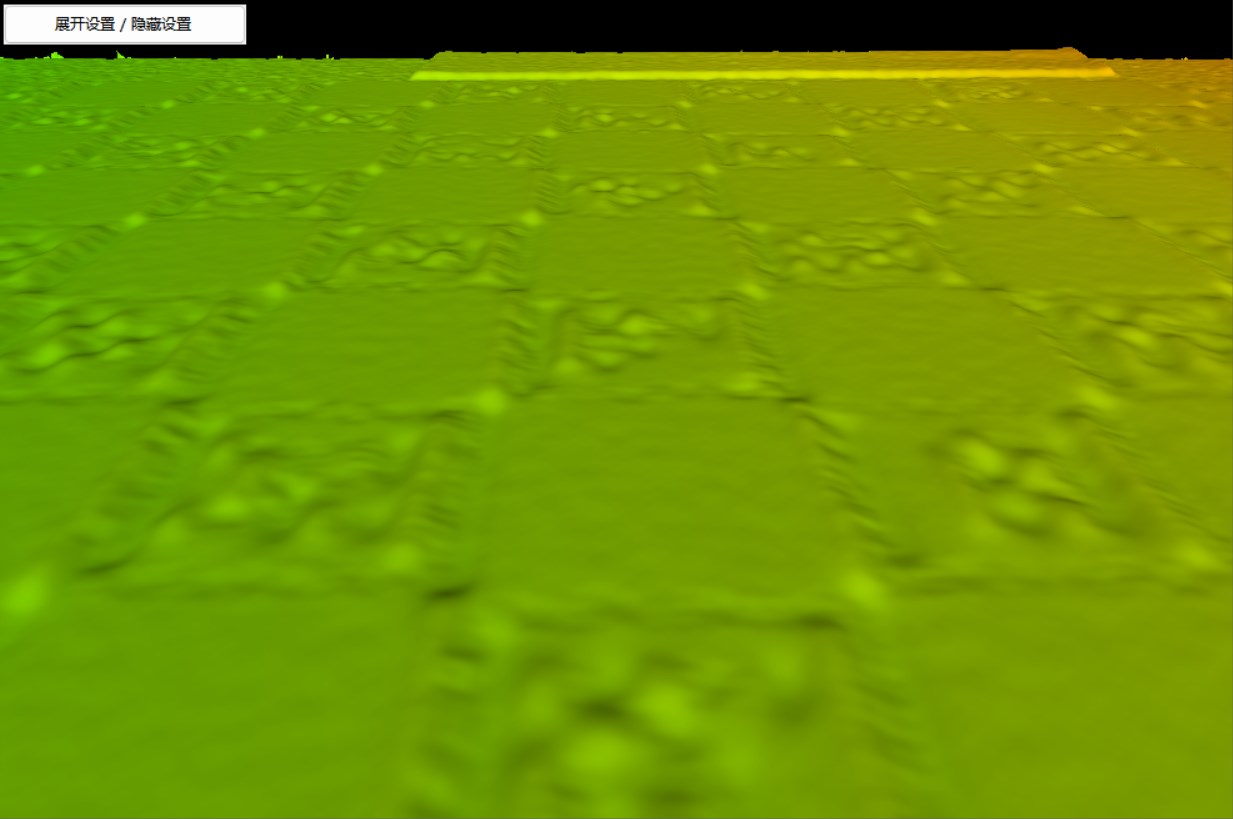 |
|---|---|
| Figure 11: Before Smoothing | Figure 12: After Smoothing |
Five modes are available, similar to removing burrs. Off means the current setting is not enabled, while Weak, Normal, Strong use the device's preset parameters. Custom means manually setting the parameters.
When Custom mode is selected, you can manually set the parameters for smoothing, as shown in Figure 13:
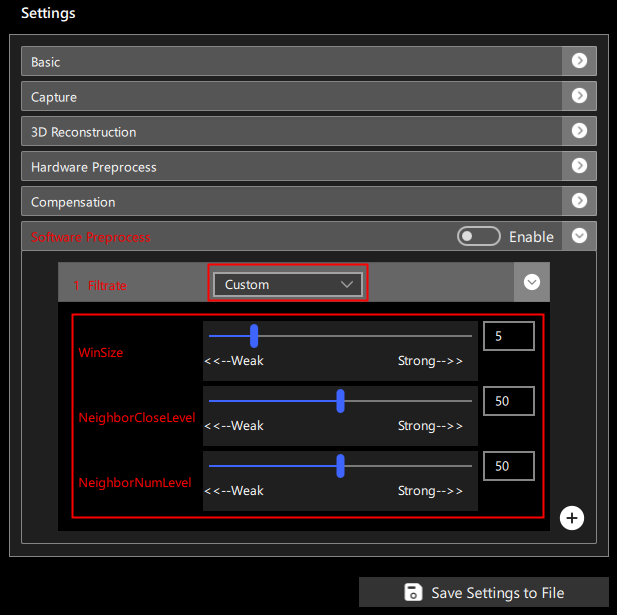
Parameters include:
-
Window Size (WinSize): The range for neighboring points, values from 0 to 31, the larger the value, the more smoothing occurs;
(Software default presets: Weak-3, Normal-5, Strong-10)
-
Neighbor Close Level: The parameter for judging the closeness of neighboring points, values from 0 to 100, the smaller the value, the more points participate in noise reduction, improving the smoothing effect;
(Software default presets: Weak-55, Normal-50, Strong-45)
-
Neighbor Num Level: The number parameter for close neighboring points, range from 0 to 100, the smaller the value, the more points participate in noise reduction, improving the smoothing effect;
(Software default presets: Weak-55, Normal-50, Strong-45)
Median Filter
The median filtering method uses statistical median of neighboring points to process 3D data, the larger the window, the larger the range of points participating in the statistics, making it easier to remove outliers.
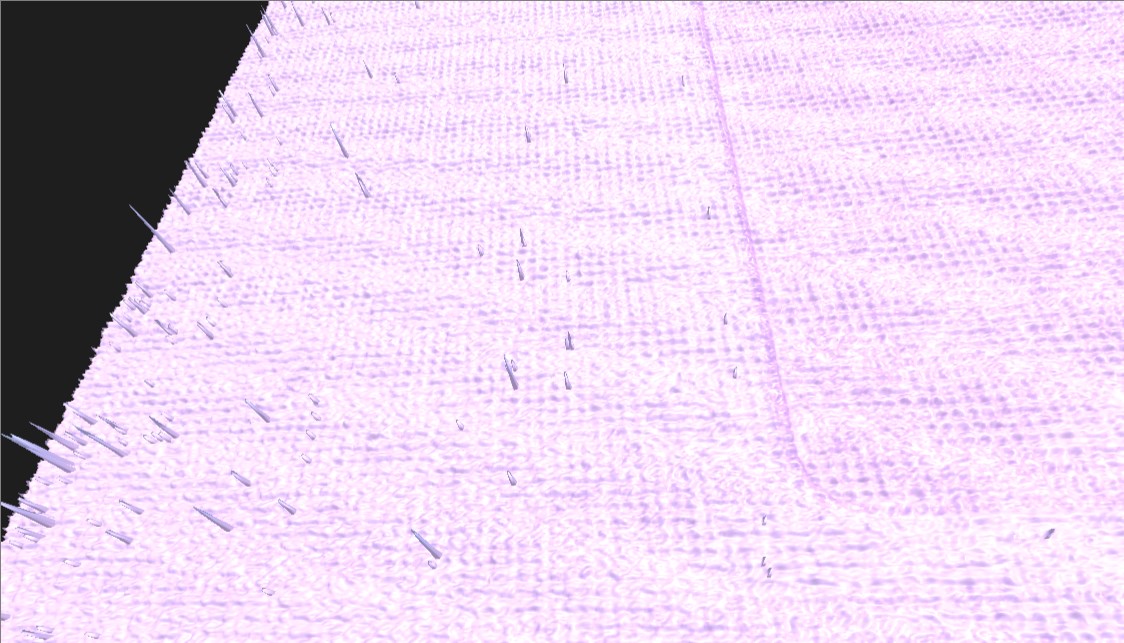 |  |
|---|---|
| Figure 14: Before Median Filtering | Figure 15: After Median Filtering |
Five modes are available, similar to smoothing. Off means the current setting is not enabled, while Weak, Normal, Strong use the device's preset parameters. Custom means manually setting the parameters.
When Custom mode is selected, you can manually set the parameters for median filtering, as shown in Figure 16:
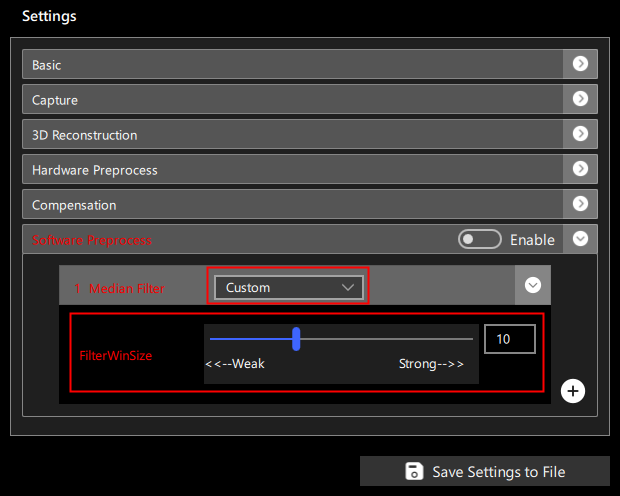
Parameters include:
-
Window Size (FilterWinSize): The range for neighboring points, values from 0 to 31, the larger the value, the more smoothing occurs;
(Software default presets: Weak-5, Normal-10, Strong-15)